August 1 News.Step StarAnnouncing the next generationbase-large model Step 3 FormalOpen SourceThe Step 3 API is now available on stepfun.com, and users can also experience it on the Step AI website (stepfun.com) and the Step AI App. experience.
According to the introduction, the multimodal capability of Step 3 is centered around "lightweight visual path" and "stable cooperative training", focusing on solving the token burden and training interference brought by the introduction of vision. To this end, it adopts 5B Vision Encoder and downsamples visual features through two-layer 2D convolution, reducing the number of visual tokens to 1/16 of the original, reducing the pressure of context length and improving inference efficiency.
1AI attached the official description of the Step 3 model as follows:
core element
- Step 3 balances intelligence and efficiency, and is designed for enterprises and developers seeking the ultimate balance of performance and cost, aiming to build the most appropriate model for applications in the age of inference.
- Step 3 utilizes the MoE architecture with 321B total parameters and 38B activated parameters.
- Step 3 possesses strong visual perception and complex reasoning ability, and can accurately complete complex knowledge understanding across domains, cross-analysis of mathematical and visual information, and various visual analysis problems in daily life.
- Through the optimization of MFA (Multi-matrix Factorization Attention) & AFD (Attention-FFN Disaggregation), the inference efficiency is greatly improved on all kinds of chips.
- The StepMesh communication library for AFD scenarios has been open sourced along with the model, providing a standard deployment interface that can be deployed across hardware to support stable reproduction of key performance in real-world services.
- In the model's limited time discount, all requests are calculated at the lowest price, as low as $1.5 per million tokens input and $4 per million tokens output.
The Step 3 API is now available on the StepFun open platform (platform.stepfun.com), and you can also experience it on the Step AI website (stepfun.com) and Step AI App (search and download in the app store). You can also experience it on the official website of "Stepfun AI" (stepfun.com) and "Stepfun AI" App (search and download in app store).
Industry-leading model performance
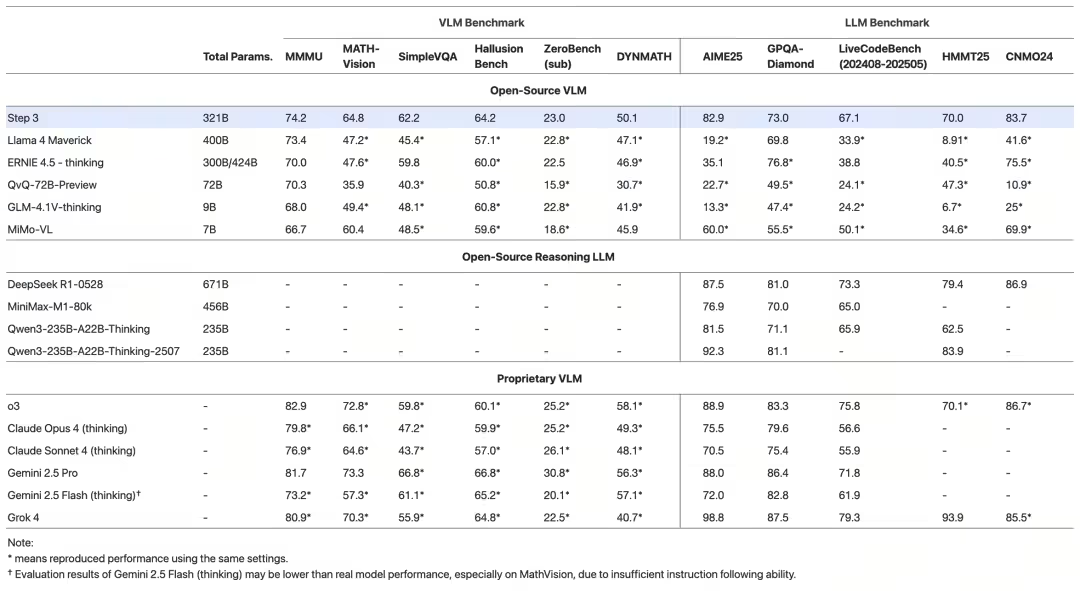
We tested Step 3 on review sets such as MMMU, MathVision, SimpleVQA, AIME 2025, GPQA-Diamond, and LiveCodeBench (2024.08-2025.05), and Step 3 scored industry-leading among open-source models of its type.
Technical Highlights
Step 3 focuses on solving the problems of multimodal collaboration, system decoding cost and inference efficiency, and makes system-level optimization on training path, architecture design and inference deployment.
1. Pre-training framework
The core structure of Step 3 adopts the self-developed MFA attention mechanism, which effectively reduces the KV cache overhead and arithmetic power consumption in attention computation. On the premise of not sacrificing the model capability, this scheme achieves a balance between resource utilization and reasoning efficiency, which enables the model to complete large-throughput reasoning on 8×48GB graphics cards, and has the feasibility of real deployment.
2. Multi-modal pre-training
The multimodal capability of Step 3 is centered on "lightweight visual path" and "stable co-training", focusing on solving the problem of token burden and training interference caused by visual introduction. To this end, we adopt 5B Vision Encoder and downsample the visual features through two-layer 2D convolution to reduce the number of visual tokens to 1/16 of the original one, reduce the pressure of context length, and improve the inference efficiency.
To ensure the stability of multimodal training, the training process is divided into two phases: the first phase strengthens the Encoder perception, and the second phase freezes the visual encoder and optimizes only the backbone and connectivity layers to reduce the gradient interference. The training corpus also needs to be matched with the strategy to guarantee stable collaboration. The multimodal corpus covers Pair, Interleave and multi-task data, and similarity filtering, resampling and task ratio control are introduced in the cleaning process to further improve the quality of graphic-text collaboration and training robustness.
3. AFD decoupling system
Step 3 Reconstruct the decoding process at the system architecture layer, focusing on solving the inference bottleneck and resource mismatch problem caused by the mixed execution of Attention and FFN. To this end, we realize a high-performance AFD (Attention-FFN Disaggregation) scheme, which decouples the two types of computation tasks into two subsystems, and improves the overall throughput efficiency through multi-stage pipeline parallel scheduling.
Due to the high demand of data transmission between decoupled subsystems, we also developed a StepMesh communication library for AFD scenarios, which realizes low latency and high bandwidth cross-card transmission based on GPU Direct RDMA, and at the same time does not consume GPU computational resources and adapts to multiple types of heterogeneous hardware, etc. The Step 3 library can be used in a 50ms decoding SLA, and its throughput reaches 4039 tokens/gpu/s on Hopper GPU. Under the SLA premise of 50ms decoding, Step 3 achieves 4039 tokens/gpu/s throughput on Hopper GPU, which is significantly higher than that of DeepSeek V3 (2324 tokens/gpu/s) with similar settings, and the performance gain is further amplified to 300% in specific hardware and long text scenarios.
The StepMesh library has been open-sourced along with the model, providing a standard deployment interface across hardware and supporting stable reproduction of key performance in real-world services. We will also actively work with the open source community to promote the above technologies so that they can be more easily adopted and utilized.