Share of the Day - "Life of Plants" AI Gameplay
A while ago when I was brushing up on videos, I found a very good blogger, making the whole lotus from the beginning of the seed to grow and mature out of the silt of the video, today just have time to dismantle everyone to learn.
Okay, no selling today, let's start tearing it down.
The whole practice only 3 steps: 1. text born map, 2. map born video (first and last frames), 3. video editing release
step by step
Step 1: The Life of a Plant Vincennes Chart ofPrompt word
Simply enter the plant name and the number of subplots and click generate. (Models we use beanbag, kimi, etc. are available)
For example: Lotus 12 would output the cue word for the 12 minute mirror sketch and the cue word for the first and last frames of the video

Here's an example of a watermelon: (subplot around 11-12, 1 subplot 5 seconds, all in 40-50 looks)
The full split-screen cue word is shared for you to learn:
1. Seed stage: ultra-high-definition realistic photography, outdoor field background. 1 flat oval watermelon seed is placed on the surface of moist brown soil, the seed coat is dark brown with light brown edges, the surface is densely covered with very fine mesh lines, and the umbilicus is slightly depressed. Soft side backlighting (such as early morning sunlight at 8:00 a.m.) illuminated from the upper left at 45°, the edge of the seed to form a light gray shadow, soil particles (diameter of about 2mm) clearly adhered to the seed coat localized, the background bokeh light yellowish-brown, highlighting the seed's flattened texture and the soil wetness.
2.Germ root germination:Ultra clear realistic photography, outdoor field background. Watermelon seed half buried in slightly moist soil (humidity about 60%), seed coat from the tip of the split about 1/4, milky white radicle (about 0.8cm long) curved down into the soil, the tip with transparent mucus layer. Soft natural light (e.g., diffuse light on a cloudy day) is projected from directly above, the mucus reflection on the surface of the radicle and the moisture (tiny water droplets) in the soil crevices are clearly visible, and the film on the inner side of the seed coat is slightly rolled over, and the lens focuses on the split to highlight the biological details at the moment of germination
3. Cotyledon emergence: superb photorealistic image, outdoor field background. 2 oval cotyledons (ca. 2 cm long) emerge from the soil, with slightly yellowish curved hooks at their tips, slightly curled cotyledon margins, and a fine, downy surface. Slanting sunlight from the right at 10 a.m. creates a triangular shadow on the soil below the cotyledons, with seed coat fragments still adhering to the base of the cotyledons, and moist soil clumps visible in the background bokeh.
4. True leaf growth: ultra-realistic photography, outdoor field background. Seedlings spread 2 palmate true leaves at the top, the edge of the leaf blade has a serrated notch, the leaf veins are light green radial distribution, the petiole is about 1.5cm long and slightly purple halo. Under diffuse light on a cloudy day, the dewdrops on the surface of the leaves refract the light, the cotyledons have become significantly larger and darker green, and the soil around the roots is slightly cracked.
5. Vine Spreading: ultra-realistic photography, outdoor field background. The main vine (about 0.8cm in diameter) grows creeping along the ground, with internodes about 8cm long, with tendrils (spirally curling) and axillary buds at each node, and short white bristles on the surface of the vine. In the afternoon, when side light is shone at 45° from the upper left, the vine casts long shadows, and the nodes touching the ground have sprouted white adventitious roots, and some tendrils are entangled in small clods of soil.
6. Female flower formation: superb photorealistic, outdoor field background. The vine bears one female flower at the leaf axil of node 8, the calyx is green and five-lobed, the petals are light yellow and obovate (about 3cm in diameter), the center of the petals reveals a light green stigma (trichotomous), and the ovary is a small ellipsoid (about 1.2cm in length) below the calyx, covered with dark green tomentum. The petal edges are tinged with morning dew when exposed to soft light in the early morning, and the female flowers are surrounded by unopened male flower buds in a tightly closed bract.
7. Pollination Moment: Ultra high definition realistic photography, outdoor field background. 1 bee stopped at the stigma of the female flower, the golden yellow pollen mass carried by its hind legs is in contact with the stigma, the petals are half-expanded, and the ovary is slightly enlarged. The sun is shining at 9:00 a.m., the transparent lines of the bee's wings and the pollen grains are clearly visible, the male flowers around the female flower are already open and the yellow anthers are dispersing pollen, and the background is blurred into a green field.
8. Young fruit formation: ultra-realistic photography, outdoor field background. Young fruit (about 3cm in diameter) 3 days after pollination are ellipsoidal, with light green skin with very fine white stripes, densely covered with white downy hairs, and tiny nodules where the fruit stalk joins the vine. Under diffused light on a cloudy day, a small amount of hay was spread on the soil below the young fruit (to prevent crushing), and 1-2 drops of rainwater remained on the pericarp, with obvious reflections.
9. Young fruit growth: superbly photorealistic, outdoor field background. Young fruits of about 10cm in diameter are half buried in loose soil, with widening dark green - light green stripes on the pericarp, the downy hairs gradually thinning out, the shape of the fruit becoming rounded, and the stalk thickening (about 0.6cm in diameter) and lignifying. In the afternoon, the sunlight penetrated through the gaps of the leaves to form light spots on the pericarp, and shallow pits appeared in the soil underneath the fruit due to weight-bearing, and the surrounding vines had already developed lateral vines.
10. Color change of rind: ultra clear realistic photography, outdoor field background. A watermelon fruit with a diameter of about 20cm, the bottom color of the rind changed from light green to dark green, the dark stripes were thickened and had a waxy luster, the umbilicus was slightly concave, and traces of delamination were formed at the base of the fruit stalk. When exposed to backlight in the evening, the edge of the rind formed a golden outline light, and the color difference between the sunny side and the shady side of the fruit was obvious, with a few small insect bite holes visible on the surface (which had already healed).
11. Fruit ripening: ultra high definition realistic photography, outdoor field background. Ripe watermelon (diameter of about 25cm) lying on the side of the field ridge, the skin dark green stripes and light green color contrast, the surface is covered with a thin layer of wax powder, the stalk is naturally curved and lignified brown. Under the top light at noon, the fruit was full and elastic, with reticulation faintly visible on the sunny side, and the rind was slightly darker in color on the lightly tapped area, and the surrounding leaves were beginning to turn yellow.
With the cue word, next we out of the map, here is just a demonstration, not to go deeper polishing, we use the beanbag batch out of the map to solve.
Bean bag batch out of the picture
Open Beanbag - Photo Production (https://www.doubao.com/chat/create-image)
Input our previous prompt words, write the requirements at the top, such as: batch generate images, ratio 9:16

Wait a little while AI all generated to complete, of course, which if encountered unsatisfactory, we can directly in the beanbag inside the generation again until satisfied.

Then we took the hold image directly and downloaded it without watermarks locally ready to come out with the video.



Step 2: i.e. dream map born video (first and last frames)
Open Instant Dream AI: https://jimeng.jianying.com/
Click on the image to generate
Click to enter a fully-generated description prompt
Click on Model Video 3.0
Be sure to use the first and last frame feature here. If you haven't modified the number of images as your teacher did, just use the cue word directly.
Here are a couple of additional screens for effect
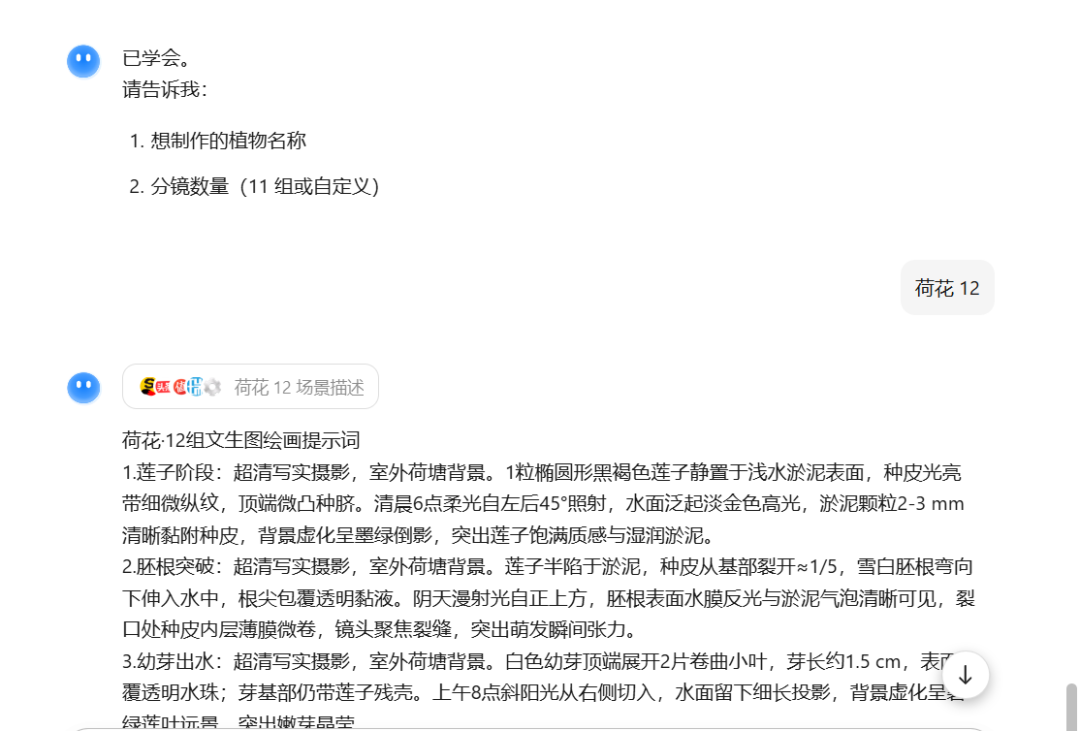
Normal demo example
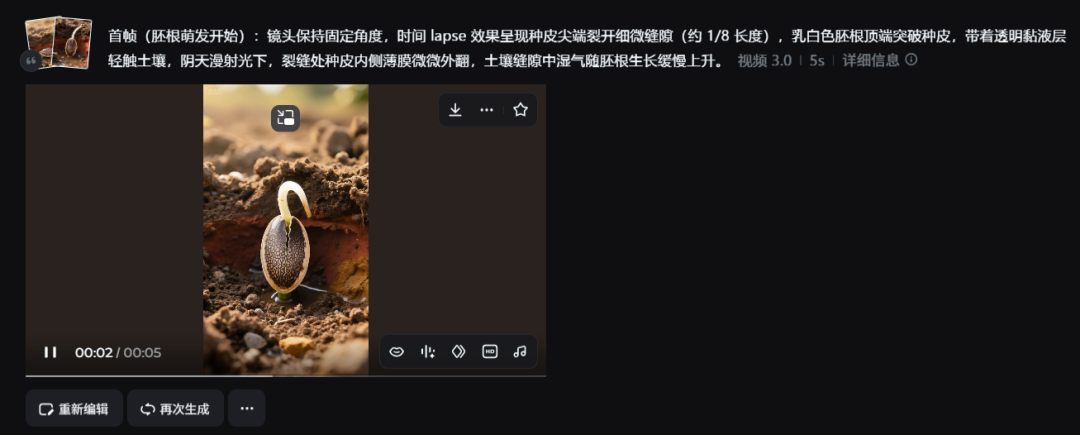
Then we follow the order of the first and last frames in order to generate the video. Simply put the first frame uploads image 1 and the last frame uploads image 2, which is 5 seconds long.
Video generates descriptors for you to share
1. Seed stage → radicle germination
- End frame (end of seed phase)The ultra-high-definition realistic lens slowly pans down to focus on the edge of the seed in contact with the soil, the seed coat is slightly swollen due to water absorption, the light brown lines on the edge of the dark brown seed coat are clearer, and under the side backlight in the early morning, the tiny droplets of water condensed in the seed umbilicus concavity reflect the shimmering light, and the moist film on the inner side of the seed coat can be seen vaguely in the place where soil particles are adhered to.
- First frame (start of germination)The lens is held at a fixed angle for a lapse of time to show a tiny slit (about 1/8 length) at the tip of the seed coat, the tip of the milky-white radicle breaks through the coat and touches the soil with a transparent mucus layer, and under diffuse light in cloudy weather, the inner membrane of the seed coat at the slit is slightly turned out, and the moisture in the soil slit slowly rises with the growth of the radicle.
2. Emergence of radicle → emergence of cotyledons
- End frame (end of radicle germination)The camera moves slowly upward from the split, the radicle has elongated to 1cm, the curvature of the radicle into the soil is more obvious, the mucus layer covers the entire radicle surface, the seed coat split is enlarged to 1/3, the inner membrane is completely rolled over, the soil is slightly cracked due to the growth of the radicle, and the soil particles can be seen in cloudy light to be slightly displaced with the movement of the radicle.
- First frame (beginning of cotyledon emergence)The camera pans up to the soil surface, where slanting early morning sunlight cuts in from the right, the soil surface is slightly elevated, the elevation is cracked with a thin slit, the light yellow curved hooks at the top of the two cotyledons have just broken through the soil, and the seed coat remnants are semi-adherent to the base of the cotyledons, and the moist clumps of soil around the edges of the cracks are carrying tiny beads of water, and shadows are spreading out at an acute angle according to the angle of the sunlight.
3. Cotyledon emergence → true leaf growth
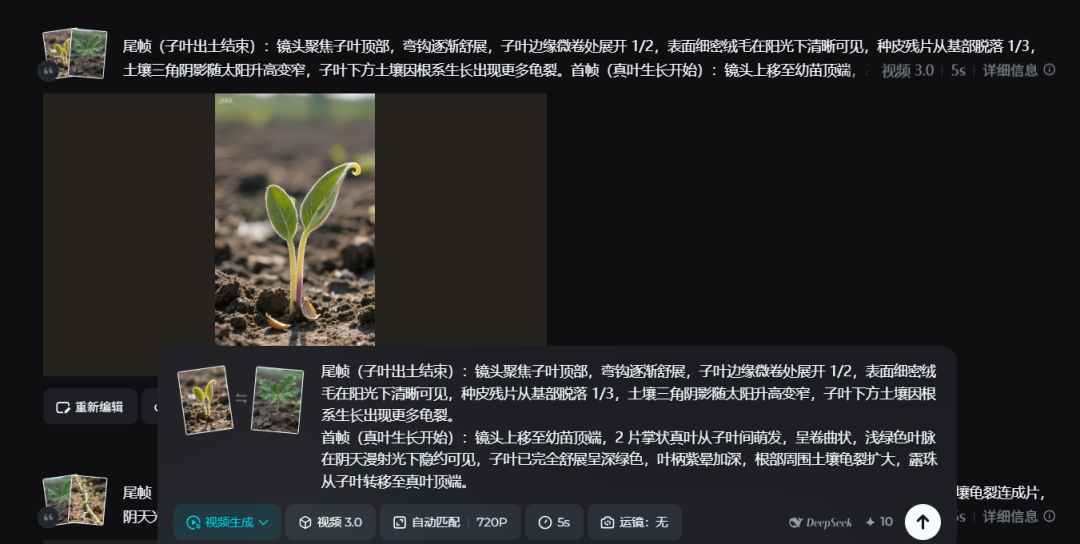
- End frame (end of cotyledon emergence)The camera focuses on the top of the cotyledons, the curved hooks gradually spread, the margins of the cotyledons are slightly rolled over and spread by 1/2, the fine surface tomentum is clearly visible in the sunlight, the seed coat debris is detached by 1/3 from the base, the triangular shadows of the soil become narrower with the sun, and the soil below the cotyledons shows more cracks due to the growth of root system.
- First frame (onset of true leaf growth)The camera pans up to the top of the seedling, where two palmate true leaves have sprouted from between the cotyledons and are curled, with light green veins faintly visible in diffuse light on a cloudy day, the cotyledons are fully expanded and dark green, the petiole has deepened in purple halo, the soil around the root has expanded in cracks, and the dewdrops have shifted from the cotyledons to the tips of the true leaves.
4. True leaf growth → vine extension
- End frame (end of true leaf growth)The camera moves slowly from the true leaves to the stems, where the serrated edges of the true leaves are fully expanded, the petioles are up to 2 cm long, the purple halo is fading, the stems are thickening to 0.5 cm, the soil at the roots is cracked and connected to the roots, and the dewdrops of the leaves are slipping off in the cloudy light, and the edges of the cotyledons are beginning to yellow.
- First frame (start of vine stretching)The main vine is creeping along the ground, the first internode has grown to 5cm, spiral tendrils are sprouting from the nodes, short white bristles are forming reflective spots in the afternoon sidelight, white adventitious rootlets are appearing at the nodes that are touching the ground, and the soil is being pushed away slightly with the movement of the vine.
5. Vine extension → female flower formation
- End frame (end of vine stretching)The camera focuses on node 7 of the vine, with internodes up to 8cm in length, tendrils fully curled and entangled in small clumps of soil, adventitious roots embedded in the soil for 1cm, and denser bristles on the surface of the vine, with patches of afternoon sunlight through the leaves moving slowly over the vine, and shadows of the vine lengthening up to 10cm in the sidelight.
- First frame (start of female flower formation)The camera advances to the axil of leaf node 8, and in the soft light of early morning, the sepals of the female flower are slightly closed, the light green stigma is hidden inside the five-lobed calyx, and the ovary fledgling (ca. 0.5 cm) has dark green hairs on its surface standing upright, while the male buds next to it are globular, with petal edges with morning dew, and the field in the background is light green in the morning light.
6. Female flower formation → pollination instant
- End frame (end of female flower formation)The female flower petals are 1/3 spread from the calyx, the light yellow petal edges are slightly trembling, the ovary is enlarged to 0.8cm, the stigma tip is slightly open, the morning dew slides off the petals in the soft morning light, and the male flower buds appear to have a tiny split at the top and are about to open.
- First frame (pollination starts instantly)A bee flies into the frame from the left, the pollen mass on its hind legs is close to the stigma, the male flower has opened and the yellow anthers are dispersing pollen, the pollen particles form a tiny column of light in the sunlight, and the field in the background is growing green.
7. Instant pollination → young fruit formation
- End frame (end of pollination moment): The camera follows the bees as they fly away, the petals of the female flowers begin to close, the stigmas are dusted with golden yellow pollen, tiny nodules appear at the base of the ovary where it joins the vine, the edges of the petals gradually lose their morning dew in the morning sun, the pollen dispersal of the staminate flowers decreases, and the anthers are slightly dried out.
- First frame (start of young fruit formation): Camera pushed into ovary area; in diffuse light on a cloudy day, young fruit 3 days after pollination is oval, with incipient white stripes on light green pericarp, white downy hairs erect on surface, and thickened stipe tubercles; soil-matted hay below is slightly sunken, and 1 droplet of rainwater rolls off pericarp and onto hay.
8. Young fruit formation → young fruit growth
- End frame (end of young fruit formation)The camera is slowly zooming out, the young fruit increases to 5 cm in diameter, the pericarp stripes widen, the tomentum remains dense, the stipe thickens to 0.4 cm, the pericarp evaporates in cloudy light leaving shallow traces of water droplets, the surrounding vines begin to develop lateral shoots, and the soil hay is slightly deformed as the young fruit gains weight.
- First frame (start of young fruit growth)Focusing on young fruits half buried in the soil, the afternoon sunlight moves through the leaf slits to form a spot on the 10 cm diameter fruit skin, with contrasting dark green-light green stripes, sparse to semi-shedding downy hairs, the first signs of lignification of the fruit stalks, a shallow crater in the soil underneath the fruit due to weight bearing, and the lateral vines have grown to 3 cm in length.
9. Young fruit growth → pericarp color change
- End frame (end of young fruit growth)The lens encircles the young fruit up to 15 cm in diameter, the pericarp stripes are stable in width, the tomentum is largely lost, the fruit stalks are lignified to brown, the afternoon light spots form alternating light and dark spots on the pericarp, the soil pits deepen, the surrounding lateral vines develop new leaves, and the edge of the leaf blade begins to touch the fruit.
- First frame (start of peel color change)The fruit is backlit in the evening, with a 20 cm diameter rind that transitions from light green to dark green, with a waxy edge to the dark stripes, tiny soil deposits in the hollow of the umbilicus, a clear color difference between the sunny and shady sides, insect-bitten holes covered with light brown tissue, and the first light brown leaves of the vine.
10. Peel color change → fruit ripening
- End frame (end of peel color transfer): The lens shifted from backlight to side light, the dark green stripes of the rind were fully set, the waxy luster was enhanced, the petiole left the layer of brown deepened, the light of the fruit outline faded in the evening light, the reticulation on the sunny side was vaguely visible, the surrounding leaves began to yellow, and the soil appeared to have more cracks due to drying.
- First frame (beginning of fruit ripening)Fruit: Focusing on a side-lying fruit in midday top light, the 25 cm diameter fruit has dark green stripes contrasting with a light green background, the surface has a matte texture in sunlight with thin wax powder, the fruit stalk is completely woody and bent, and the skin is slightly sunken and then bounces back after tapping the area, and the surrounding yellowish leaves drift down to the soil surface in 1 or 2 pieces.
Step 3: Edit the finished product
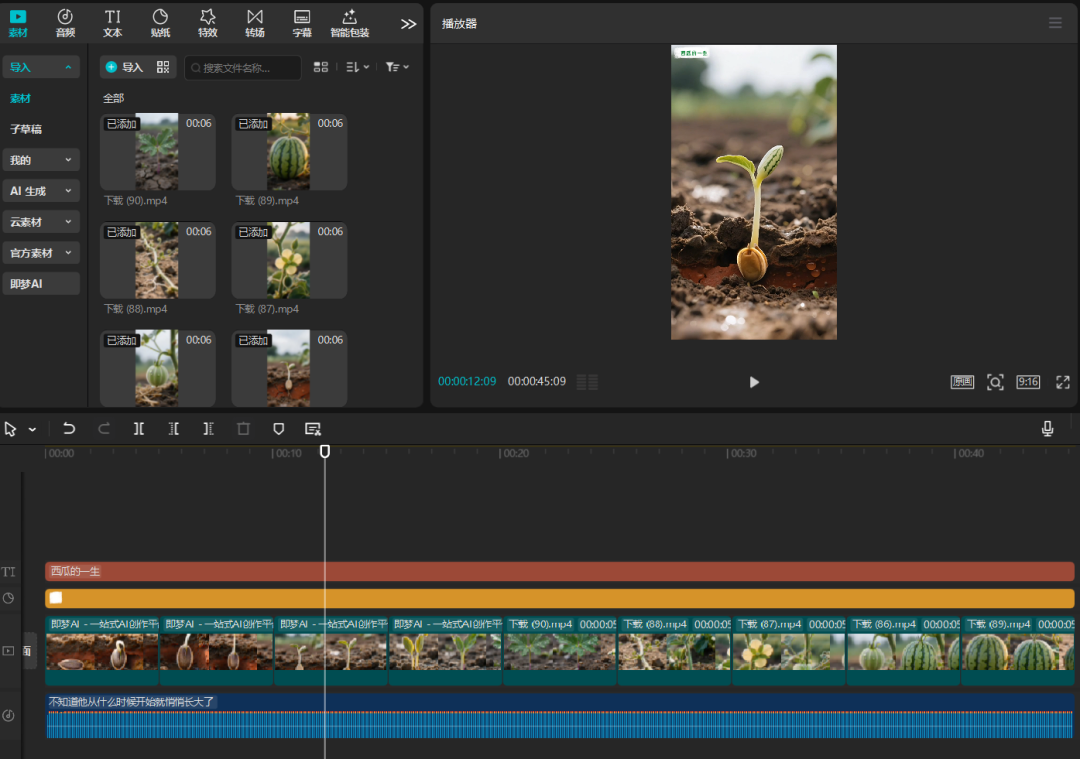
After generating a good direct cut out of the film can be imported into our clip video with BGM on completion.
Test Points: The video is mainly about the growing process of the plant, adding ground effect and mentioning the hardy generation of the plant is the core. It costs more points. Play the basic logic and practical understanding, we should go to the innovative production of some characteristics of the video, to maintain a continuous release, burst of fire is a matter of time. Do not start looking at others fire, thinking that can be too explosive.
Difficulty of practice: ★★★★★★
Tools and methods have the last is also a test of perseverance and creativity, the lack of one can not~
That's what I'm sharing today.Everyone can get hands-on, easy to learn, hurry up and try it~!